Web Application Configuration
Web applications consist of static content (HTML, images) as well as dynamic content (Servlets, JSP's and Java Classes), normally a system administrator although does not program them, will normally deploy them, so a basic understanding on how Web applications work will help.
Web applications configuration can be broken down into two area's
The Contents of a Web Application
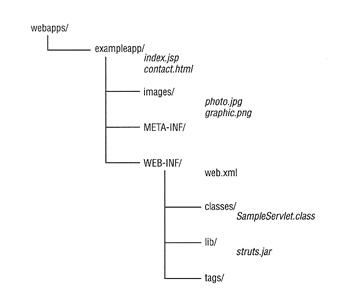
Web applications are normally installed under the webapps directory in Tomcats home directory, the basic structure is below

You can access this by using the URL http://localhost/exampleapp, were /exampleapp/ is called the context path for the Web application. The minimum requirement is WEB-INF directory with a web.xml file in it. By default index.jsp is used if no web page is requested followed index.html then index.htm.
Everything outside the WEB-INF and META-INF directories are public resources, and can be accessed via a URL. The WEB-INF and META-INF directories are private only to the Web application itself and cannot be accessed via a URL.
URL mappings
A URL mapping maps a URL to a servlet using a number of elements, the best way to explain this is by an example
| URL mapping example | <servlet> <servlet-mapping> |
I the example above all *.jsp files are mapped to a servlet named jsp which itself points to the JspServlet class. The load-on-startup means that the Servlet class is loaded into memory on startup with a priority of 3 (1 being the highest) to ensure that it is loaded before any JSP pages are requested.
You can use three types of URL mapping
WEB-INF Directory
The three subdirectories in the above example Tomcat directory structure, are used for the following
| classes directory | this directory contains servlets and utility classes, including JavaBeans. It could also contain a number of resource files (key/value pairs). The classes are stored in the normal directory hierarchy structure, so uk.co.datadisk.DatabaseServlet would be stored in uk/co/datadisk directory. As mentioned a number of resources files normally with a extension of .properties can be kepted here. The files placed in this directory are only accessible by the Web application. |
| tags directory | This directory will contain tag libraries, a tag library is a group of Java classes that define the functionality of dynamic markup tags. Tag libraries will have a .tld extension. |
| lib directory | This directory contains the Java libraries (.jar files) that the Web application requires. The files in this directory are only accessible to the Web application. |
META-INF Directory
A Web application may have an optional META-INF directory that contains deployment information for tools that create war files and resources that applications may rely on. This is only accessible by the Web application and is private. It may contain two configuration files manifest.mf and the context.xml file.
The manifest.mf file is an optional configuration file for the Web application, it contains a list of JAR files on which an application relies, the container can use this to check for all the required libraries that are to be made available for the Web application.
| Example manifest.mf file | Extension-List: extension1 extension2 extension3 |
The manifest file is generally created when a Web application is packaged as a Web Archive (.war file)
The context file contains the configuration for the Web application Context, see Tomcat Architecture for more information on this file.
The Deployment Descriptor (web.xml)
A deployment descriptor is an XML file that contains configuration information used by the Web application for execution on the Servlet Engine. There is a global version of this file (web.xml) in the conf directory, this file applies to all Web applications.
There are three three different versions of this file that support Servlet specification 2.3, 2.4 and 2.5. In version 2.3 it uses a Document Type Definition (DTD) style, where as 2.4 and 2.5 use a schema style.
2.3 version (DTD style) |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN" "http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.data"> <web-app> ... </web-app> |
2.4 version (Schema style) |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <web-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee web-app_2_4.xsd" Version="2.4"> ... </web-app> |
2.5 version (Schema style) |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <web-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_5.xsd" Version="2.5"> ... </web-app> |
Servlet 2.3 Style Deployment Descriptor
The web.xml takes the below form
2.3 Version (web.xml) |
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN" "http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.data"> <web-app> <icon> <display-name> <description> <distributable> <context-param> <filter> <filter-mapping> <listener> <servlet> <servlet-mapping> <session-config> <mime-mapping> <welcome-file-list> <error-page> <taglib> <resource-env-ref> <resource-ref> <security-constraint> <login-config> <security-role> <env-entry> <ejb-ref> <ejb-local-ref> </web-app> |
The order of the components inside the <web-app> elements must be shown as above, some of the elements are optional. I am going to give a basic description and a simple example of each element, you can find more details on the Internet for a more in depth description of each element.
<web-app> Elements - Version 2.3 |
||
| Element | Description | Required? |
| icon | Image for an application | 0 or 1 |
| display-name | Display name for a Web application | 0 or 1 |
| description | Description used for display | 0 or 1 |
| distributable | A boolean value indicating whether an application is distributable across servers (clustering) | 0 or 1 |
| context-param | Initialization parameters for the entire Web application | 0 or more |
| filter | Defines a filter Valve | 0 or more |
| filter-mapping | Defines a URL pattern to which the given filter needs to be applied | 0 or more |
| listener | Defines a lifecycle event listener | 0 or more |
| servlet | Defines a servlet | 0 or more |
| servlet-mapping | Defines a URL pattern to invoke a named servlet | 0 or more |
| session-config | Defines session configuration | 0 or 1 |
| mime-mapping | Defines the MIME type for a given file type | 0 or more |
| welcome-file-list | A list of files to be served if no resource is specified by the URL | 0 or 1 |
| error-page | Defines a Java exception or an HTTP code-based error page | 0 or more |
| taglib | Declares a tag library | 0 or more |
| resource-env-ref | Declares a resource-administered object | 0 or more |
| resource-ref | Declares an external resource | 0 or more |
| security-constraint | Restricts access to a resource to a required transport guarantee and by user role | 0 or more |
| login-config | Defines authentication parameters | 0 or 1 |
| security-role | Declares a security-role by name | 0 or more |
| env-entry | Defines a Web application's environment entry | 0 or more |
| ejb-ref | Declares a reference to an EJB's home | 0 or more |
| ejb-local-ref | Declares a reference to an EJB's local home | 0 or more |
Examples |
||
| icon | <icon> <small-icon>/images/icons/small.gif</small-icon> <large-icon>/images/icons/large.gif</large-icon> </icon> |
|
| display-name | <display-name>Example Application</display-name> | |
| description | <description> This is datadisk's example application used for demo purposes hope you enjoy </description> |
|
| distributable | <distributable>true</distributable> Note: by default it is set to false |
|
| context-param | <context-param> Note: you can have many of these context-params, they are just key-value pairs that can be used by the Web application |
|
| filter | <filter> Note: as you can see the <filter> element has many subelements that can be used, see the <filter-mapping> to how you map your filter |
|
| filter-mapping | <filter-mapping> <filter-name>Compressor</filter-name> <url-pattern>*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> |
|
| listener | <listener> Note: see Tomcat advanced features for more information on listeners |
|
| servlet | <servlet> <!-- you can use a JSP file instead of a servlet |
|
| servlet-mapping | <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>downloadServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/download/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> |
|
| session-config | <session-config> Note: there are a number of other subelements you can use i.e <timer-keep-alive> |
|
| mime-mapping | <mime-mapping> Note: there will be lots of different mime-type settings |
|
| welcome-file-list | <welcome-file-list> Note: the above is the default anyway, but you can configure whatever you want |
|
| error-page | <error-page> <error-code>404</error-code> <location>/errors/404.jsp</location> </error-page> <error-page> <error-code>java.lang.NullPointerException</error-code> <location>/errors/badcode.jsp</location> </error-page> |
|
| taglib | <taglib> <taglib-uri>applications</taglib-url> <taglib-location>/WEB-INF/tlds/web-app.tld</taglib-location> </taglib> |
|
| resource-env-ref | ||
| resource-ref | <resource-ref> <res-ref-name>mail/Session</res-ref-name> <res-type>javax.mail.Session</res-type> <res-auth>Container<res-auth> </resource-ref> |
|
| security-constraint | <security-constraint> <display-name>Name String</display-name> <web-resource-collection> <web-resource-name>GETServlet</web-resource-name> <description>some description</description> <url-pattern>/servlet/*</url-pattern> <http-method>GET</http-method> </web-resource-collection> <auth-constraint> <description>some description</description> <role-name>*</role-name> </auth-constraint> <user-data-constraint> <description>some description</description> <transport-guarantee>INTEGRAL</transport-guarantee> </user-data-constraint> </security-constraint> |
|
| login-config | <login-config> <auth-method>FORM</auth-method> <realm-name>MemoryRealm</realm-name> <form-login-config> <form-login-page>login.jsp</form-login-page> <form-error-page>notAuthenticated.jsp</form-error-page> </form-login-config> </login-config> |
|
| security-role | <security-role> Note: security is discussed here |
|
| env-entry | <env-entry> Note: in the java code you would use something like below to obtain the value /* Obtain the initial context */ |
|
| ejb-ref | <ejb-ref> Note: I discuss MBeans here |
|
| ejb-local-ref | ||
Servlet 2.4/2.5 Style Deployment Descriptor
Servlet 2.4 and 2.5 are very similar, so i cover them together, the first difference to 2.3 is that the elements can be in any order but they are all still contained in the <web-app> element. I am only going to show example if different from version 2.3.
<web-app> Elements - Version 2.4/2.5 |
||
| Element | Description | Required? |
| context-param | Contains the Web applications Servlet context initialization parameters |
These are the same as above in the version 2.3 |
| description | Provides a description for the Web application | |
| display-name | Specifies a short name for the Web application | |
| distributable | Indicates that this Web application is programmed to be deployed in a distributed Servlet container | |
| ejb-local-ref | Declares a reference to the Enterprise bean's (EJB) local home | |
| ejb-ref | Declares the references to the JB's home | |
| env-entry | Declares the Web applications environment entries | |
| error-page | Defines a mapping between an error code or exception and an error page | |
| filter | Declares and configures a filter for the Web app | |
| filter-mapping | Specifies the filters to be applied to the Web app, and the order in which they are applied | |
| icon | Specifies filenames for icons used to represent the parent elements | |
| jsp-config | Specifies global configuration properties for the JSP pages in the Web app | |
| listener | Configures the properties of an application listener bean | |
| locale-encoding-mapping-list | Specifies the mapping between locales and their encoding | |
| login-config | Specifies the authentication methods to be used for accessing the Web application | |
| message-destination | Specifies a message destination | |
| message-destination-ref | Contains the deployment components reference to a message destination | |
| mime-mapping | Defines the mapping between an extension and a MIME type | |
| resource-env-ref | Contains a reference to an administered object associated with a resource | |
| resource-ref | Contains a reference to an external resource | |
| security-constraint | Specifies security constraints for one or more groups of web resources | |
| security-role | Defines the security roles used in the security-constraint element | |
| service-ref | Contains the reference to a Web service | |
| servlet | Configuration for a servlet | |
| servlet-mapping | Specifies the mapping between a servlet and URL pattern | |
| session-config | Defines the session parameters for the Web application | |
| welcome-file-list | Specifies a list of welcome files for a Web application | |
Examples |
||
| display-name | <display-name xml-lang="en">Examples<display-name> | |
| jsp-config | <jsp-config> ... <taglib> <taglib-uri>http://jakarta.apache.org/tomcat/examples-taglib</taglib-uri> taglib-location>/WEB-INF/jsp/example-taglib.tld</taglib-location> </taglib> ... <jsp-property-group> <description>some description</description> <display-name>JSP Configuration</display-name> <url-pattern>/jsp2/misc/config.jsp</url-pattern> <el-ignored>true</el-ignored> <page-encoding>ISO-8859-1</page-encoding> <scripting-invalid>true</scripting-invalid> <include-prelude>/jsp2/misc/prelude.jspf</include-prelude> <include-coda>/jsp2/misc/coda.jspf</include-coda> </jsp-property-group> </jsp-config> |
|
| locale-encoding-mapping-list | <locale-encoding-mapping-list> <locale-encoding-mapping> <locale>en</locale> <encoding>en_US</encoding> </locale-encoding-mapping> </locale-encoding-mapping-list> |
|